In almost any Russian park in the summer you can see beautiful flowering shrubs belonging to various botanical species. One of the popular cultures is hydrangia, the beautiful inflorescences of which can be admired for most of the warm season. The article is devoted to the most decorative representative of the family - large-leaved hydrangea, it describes the popular varieties, and gives recommendations for planting and caring for the plant.
Botanical description of the species
Garden hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla) refers to deciduous shrubs. The birthplace of culture is East and South Asia. The macrophile reaches a height of 80–150 cm. It forms flowers collected in spherical large inflorescences with a diameter of 15–25 cm.
The color of the petals can be pink, bluish, purple or white. This greatly depends on the reaction of the soil, but the presence of aluminum sulfate in the substrate is a decisive factor for the appearance of the shade. In an acidic environment it is blue, in an alkaline medium it is pink. The leaves of hydrangia are large, oval or round, rather thick, serrated, green. Flowering season: June, July, August, sometimes September.
Use in landscape design
The shrub is extremely decorative, as it has dense, bright foliage and blooms for a long time. Planted it in single and group plantings or placed along garden paths, near the terrace, next to a bench or gazebo. Macrophile inflorescences are suitable for cutting, stand in water for a long time without losing elasticity, and after drying they can be used for winter bouquets. This type of hydrangea is also grown as a houseplant, accelerating the opening of buds for spring holidays (Easter or March 8).

Popular varieties
If the owner responsibly approaches the choice of hydrangea varieties, then the garden will be decorated with large inflorescences throughout the summer months. Varieties can be combined both in plant height and in petal color. They can contrast or complement each other. Neighboring shrubs with white and bright pink (blue) buds look very impressive.
Countess Kossel
One of the earliest large-leaf varieties, revealing the first buds in early July. They are collected in huge round inflorescences up to 25 cm in diameter. At the beginning of the growing season, the petals are snow-white, but gradually turn pink along the edge and eventually become crimson.
Hydrangea branches abundantly grow large green leaves throughout the entire warm period. The variety blooms on old shoots, it develops well in the sun and in partial shade. Loves moisture and loose substrate. Resistance to frost at Grafin Cosel is average, without prejudice to the aerial parts (subject to additional shelter), can withstand minus temperatures from -20 ...- 23 ° C.
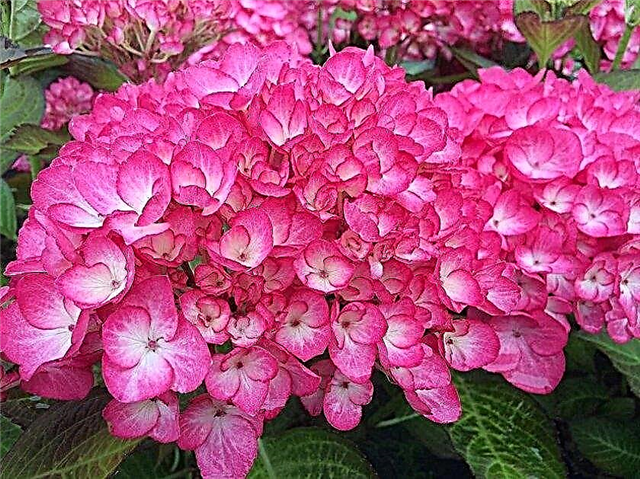 The height of the shrub is 100-120 cm, the size across is 90-120 cm.
The height of the shrub is 100-120 cm, the size across is 90-120 cm.
Magic Amethyst
An unusual variety of hydrangea with an unstable color of petals that gradually change color from lemon to pink and stop on a coral with a pale green border. Inflorescences consist of 80–90 small flowers collected in huge round balls and framed by green rounded leaves. Their severity bends the branches to the ground, therefore, it is recommended to grow the Magic Amethyst in a garter to an additional support.
The buds open from July to September inclusive. Frost resistance is weak, up to -23 ° C, so hydrangea requires additional shelter for the winter. It is characterized by good resistance to powdery mildew, which is often found on crops in wet periods.
 Size of an adult shrub: width - from 90 to 120 cm, diameter - from 60 to 90 cm.
Size of an adult shrub: width - from 90 to 120 cm, diameter - from 60 to 90 cm.
Runaway Bride
This variety belongs to the most decorative representatives of culture. The height of the Runaway Bride does not exceed 120 cm, the crown of the bush grows to a meter. Unlike most varieties, it forms not the only inflorescence at the tip of the shoot, but several (up to six pieces) developing from each lateral bud on the top of the branch. Petals of buds of white color, with a slight pink tint. The leaves are small, green, elliptical. In 2018, the variety received an award at a thematic exhibition in Chelsea (England).
The runaway bride has poor resistance to frost, so it would be wiser to grow a bush in a container and transfer it to storage for the winter. Suitable for planting in open ground mainly in the southern regions.
 The second name is Snow White. Flowering occurs in June and continues through August.
The second name is Snow White. Flowering occurs in June and continues through August.
Sybil
It belongs to medium-sized varieties (50–90 cm) with the same bush diameter. Sibilla is known among connoisseurs of culture for its large dark pink or red inflorescences. In an acidic environment, their color changes to blue-violet. Green rounded leaves are large, up to 10 cm across.
The fruit buds of Sibylla are formed in the previous season. Can be grown in a room or outdoors in containers and pots. He loves the sun and partial shade, as well as well-drained, moist soil. Without winter shelter, the aerial part of the plant freezes, which eliminates the appearance of buds next year. The variety has medium frost resistance (up to -23 ° C).
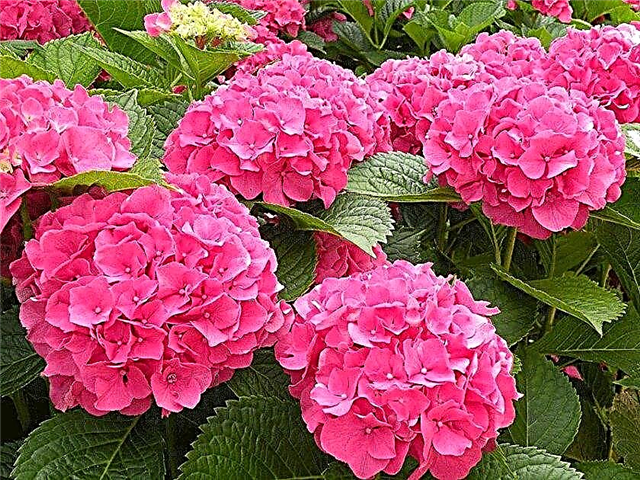 Flowering occurs in July and lasts until September.
Flowering occurs in July and lasts until September.
Twist and Shout
The height and width of the crown of an adult shrub Twist and Shout are always approximately the same, their sizes are 90-120 cm. The shoots are decorated with large oval leaf blades with a serrated edge, in the summer a dark green color, with the advent of autumn changing it to burgundy.
Numerous blue or pink buds are collected in spherical groups. Their shade depends on the pH of the soil of the flower bed. Inflorescences are medium, with a diameter of 100 to 160 mm, bloom in the summer, from June to August. Twist and Shout has low frost resistance, therefore, requires winter shelter.
 It actively forms fruit buds both on last year's branches and on the processes of this season.
It actively forms fruit buds both on last year's branches and on the processes of this season.
Hamburg
A sprawling shrub with vertical branches densely covered with round green leaves. Its width and height are approximately equivalent, from 60 to 100 cm. The plant groups spherical formations consisting of many small flowers with petals of blue or pink hue. Growing a variety in a neutral environment gives them a coral color, but if the roots are in acidic soil - blue or dark blue. The laying of fruit buds occurs in the previous season.
 The aboveground part requires additional shelter for the winter.
The aboveground part requires additional shelter for the winter.
Marmalade
A tall variety of hydrangea, often reaches 150 cm in height. Rounded saturated green leaves are pointed. Spherical inflorescences (up to 25 cm in diameter) consist of several dozen large buds with bright pink petals that do not fade under the sun. They bloom gradually, starting in mid-June. This period continues until the beginning of September.
 Marmalade has good winter hardiness (up to -25 ° C), so it does not need shelter.
Marmalade has good winter hardiness (up to -25 ° C), so it does not need shelter.
U & mi Tughese
Hydrangea macrophylla You & Me Together will bloom throughout the summer months, sometimes grabbing the first decade of September. He does not like radical pruning of the aerial parts, since fruit buds are formed on old branches in the previous year of vegetation. The bush has a spherical shape in adulthood (3 years after planting), reaching a height of 80 cm.
The petals of the buds of Yu and mi Tughese are very beautiful, terry, collected in rounded inflorescences (up to 20 cm in diameter). The shrub is quite frost-resistant and can withstand cold up to -25 ° C, so in the middle of Russia and in the south it is grown without warming for the winter.
 The leaves are dark green, ovoid, large, with a serrated edge.
The leaves are dark green, ovoid, large, with a serrated edge.
Planting large-leaved hydrangea
So that a small seedling can quickly develop and form into a beautiful, sprawling shrub, the owner of the flower bed should plant it correctly. It is advisable to carry out the procedure taking into account all the requirements of the culture. If you choose the wrong location - the plant will not be able to fully reveal all the decorative qualities. It is also very important to provide hydrangeas with a suitable soil in which its roots will be located for many years.
Seat selection
Large-leaved hydrangea grows on fertile, moist, slightly acidic soils. Significantly lags in growth if planted on dry and sandy soil. Alkaline reaction of the substrate can cause a serious disease - chlorosis. Like all other hydrangeas, it does not tolerate cold, heavy and clay soil. Likes to be located in the sun or in light partial shade.

Soil preparation
A few days before planting, the selected place is dug up. If there is a need to combat perennial rhizomes of weeds, it is worth 2 weeks before the date of work to treat the surface of the flowerbed with herbicides ("Hurricane", "Roundup"). In the event that the soil on the site does not meet the requirements of hydrangea, it is recommended to purchase several packages of a suitable substrate in advance in the garden store.
When several plants are to be planted, suitable soil can be prepared independently. Hydrangeas love light, acidic soil, rich in humus. The substrate can be obtained by mixing ground peat, crushed turf, humus, chernozem and coarse river sand in equal parts.

Landing process
In order for the plant to take root painlessly and quickly adapt, a person needs to plant a shrub correctly. When a decision is made to create an alley of hydrangeas, do not place them closer than 100-120 cm from each other. A considerable distance is due to the fact that adult hydrangia have a vast aerial part.
Important! In the year of planting, the young plant needs to be moistened about once every 7–12 days, depending on the weather.
Landing:
- First of all, it is necessary to prepare a landing pit of sufficient width and depth, where the root system of the seedling should freely fit, without compression and tightness. It is recommended that the recess be 20-30 cm wider in all directions than required. Since the gaps will be filled with loose fertile soil, then in the future the bush will be able to grow young roots without interference. The bottom of the recess is covered with ground peat.
- If the seedling has a closed root system and is in the pot, it is carefully removed, after tapping the walls and bottom of the container.
- When hydrangea with open roots is purchased, the owner should carefully examine them and remove old and diseased fragments using a garden pruner.
- The moved bush is installed in the middle of the planting pit, the roots are evenly spread, and they are covered with specially prepared soil. Water abundantly, using at least a bucket of water, and wait until the moisture is completely absorbed into the ground.
- Moistened soil usually settles significantly, so you need to add additional soil to the pit.
- Further, the surface in the near-trunk zone is compacted, trying to simultaneously form a small near-trunk recess to delay irrigation water.
- At the end of planting, the seedling is watered again, but sparingly, using 3-5 liters of water.

Care
An ornamental shrub will annually, over many months, adorn the garden with numerous inflorescences, but subject to full and timely care. The plant needs timely winter warming. If during the shelter you do not adhere to the recommended deadlines, it will die from freezing or from mold and rot. Pruning errors will result in loss of fruiting kidneys.
Watering and mulching
During the growing season, large-leaved hydrangeas should be regularly watered. During periods of drought, water should be supplied in abundance, since its shortage quickly becomes visible to the naked eye - the bush fades.
Important! A gardener can give hydrangea petals a blue tint if every 7–10 days will water the plant with a solution of alum or sprinkle them in a dry form at the roots. In this case, uniform coloring rarely occurs, as a result of which the shrub is decorated simultaneously with pink, blue and purple inflorescences, which looks very beautiful.
So that moisture lingers in the root zone and does not evaporate quickly under the influence of high temperatures, gardeners are advised to use mulching of the trunk space. This technique accepts both organic substances that gradually decompose in the soil, and artificial materials that do not allow sunlight.

Mulch Options:
- sawdust or shavings of conifers;
- last year's leaves;
- chopped straw;
- dry grass;
- spanbond;
- agrofibre.
An important condition is the complete permeability of the coating to moisture and air. Mulch should in no case interfere with watering the bush and the penetration of oxygen to the roots.
Did you know? The generic name of hydrangea comes from two Greek words hydor - water and aggeion - vessel. It symbolizes the extraordinary appetite of hydrangia for moisture.
Top dressing
If the gardener prefers to use organic matter, then in autumn, at the end of the warm season, it is necessary to decompose compost or well-ripened humus around the near-trunk zone of the plant. 10 kg of fertilizer is enough for 1 m². You can buy ready-made preparations for hydrangea nutrition in specialized stores, which are created taking into account all the requirements of the culture for minerals and acidity.

Fertilizers for hydrangea:
- Liquid concentrate of mineral fertilizers "Agrecol Biohumus" will supply nutrients to the root and aerial parts of the plant. Every two weeks, the bush is watered with the prepared solution: pour 10 ml of the drug into 1 liter of water and mix thoroughly. Use from spring to October inclusive. Top dressing will give a rich shade to the petals and leaves, provide a long flowering period.
- Mineral granular top dressing "Aqua Agricola" is suitable for use on all varieties of culture. It contains elements such as 20% potassium, 12% nitrogen and 6% phosphorus, which positively affect the appearance of shrubs and the formation of numerous fruit buds. The drug acidifies the soil, which creates additional favorable conditions for the development of hydrangea. Fertilizer is scattered in the root zone and mixed with the topsoil. The first procedure is carried out in the spring, in March, all subsequent ones with an interval of 30-60 days. It is advisable to stop the introduction of granules in the first decade of August.
- Nutritional Gels ("Royal mix", "Agrecol hortensji") allow you to give an increased portion of fertilizer in a limited volume of liquid for leaf feeding of the bush. This is especially true for sick and weakened plants in need of growth stimulation. They are used, starting in spring and throughout the growing season. The use of this form of top dressing is much more effective compared to other drugs, since 1 liter of gel can be dissolved in 1 liter of water for irrigation. In early summer, the substance is fed to the roots in the form of a nutrient mixture. During the opening of the buds, this is done once every two weeks, then one procedure per month. Its regular use provides the formation of numerous inflorescences with bright colors.

Trimming and Shaping
This culture is easily propagated by grassy cuttings, that is, not lignified shoots. Their full rooting takes about 6-8 weeks. The most favorable period for carrying out these works will be June.
A macrophile usually forms fruit buds a year before the formation of inflorescences, so in the spring the gardener should limit himself to pruning dry fragments and dead branches. A healing haircut of the aerial part is also carried out if signs of the development of fungal diseases, for example, mold, are noticed on the shoots. At the same time, diseased branches are cut out from the ground itself, completely.
If the crown needs to be formed, for this you will have to partially sacrifice the flowering of the current or next year. After all, when the branches are cut, then the buds, which should form the flowers this or next season, are also removed. The consequences will depend on the time of the operation (before or after flowering).

Winter preparations
Since most fruit buds formed last summer are in the upper part of the shoots, it may happen that a frozen shrub grows leaves and young branches safely in spring, but does not bloom. Given this feature, before the arrival of winter, it is worth covering the aerial part of hydrangy with coniferous spruce branches, several layers of agrofibre or straw mats. Before starting insulation, it is recommended to bend the branches of the shrub to the ground and fix in this position with bricks or metal studs.
Important! Summer hydration of the hydrangea root zone should be gradually reduced and completed by early August. Thus, the plant will be assisted in preparing for wintering and transition to a dormant state.
Hydrangea roots can be protected from freezing by filling the surface of the soil in the near-stem circle with a thick layer (10-15 cm) of mulch from sawdust or peat. With the advent of spring, soil warming must be removed, as it will interfere with the warming of the root system.

Features of growing at home
The plant feels rather well in indoor conditions, but only if hydrangia is provided with good lighting, suitable air temperature (above + 20 ° C) and humidity. If it is improperly looked after, diseases can occur. Excessive dryness leads to the population of the shrub with a spider mite. Darkness and high humidity in home cultivation lead to the development of fungal diseases.
Breeding methods
Hydrangea is a culture that is easy to propagate. There are several technologies designed for experienced and novice gardeners. But immediately get a young plant does not work, it will take a fairly long period. The exception is only the division of the maternal rhizome.
Cuttings
For successful propagation by this method, the gardener needs to prepare a substrate consisting of equal parts of soil for hydrangea and sand. A nursery with bulk soil is placed in partial shade, for example, under the crown of a tree. Cuttings are cut in June, each should have at least three kidneys. The upper cut on them is done horizontally, and the bottom - at an angle of 45 degrees, the leaves are completely or partially removed. Seedlings are planted in the school, abundantly watered and covered from the sun with foil or dense agrofibre.
For full rooting, it will take from two to three months, during which time the earth in the root zone of young plants should always remain slightly moist. Since the nursery is stationary and located on the street, the growing cuttings need to be safely covered for the winter. A transplant of new hydrangeas should be carried out next spring.
Did you know? The first living hydrangea samples were brought to Britain from China by the famous English naturalist Sir Joseph Banks in 1789. Picturesque shrubs quickly gained popularity and took root in the gardens and parks of the country.
Layering
To obtain a seedling using this method, one of the branches of growing hydrangia is bent to the ground and fixed in this position (with a stone, brick, metal stud). In a place where the shoot is in contact with the soil, about a bucket of soil is poured so that the shoot is well covered. After about a year, it will be well rooted and will be suitable for independent growth. The gardener will only have to cut off the young bush from the mother's "umbilical cord" and move it to a permanent place.
Dividing the bush
This is the fastest way to get some adult plants.. It is recommended to choose a highly overgrown uterine bush no younger than 5 years old. Using a sharp gardening shovel, the lateral parts of the rhizome are separated and scooped up, carefully inspecting and removing rotten or too old roots, and then transplanted to new places.

Diseases and their treatment
Under inappropriate conditions, hydrangea may become moldy. The disease is caused by spores of fungi. If the bush is properly planted and well supplied with nutrients, fungal diseases can be found quite rarely. Mold develops rapidly under the influence of strong temperature fluctuations in one direction or another. In this case, you should act quickly: remove the affected parts of the plant and burn, then treat the branches and leaves with preparations containing fungicide. If treatment is neglected, hydrangia will die.
Did you know? The genus Hydrangea includes about eighty species that drop leaves for the winter. This group has ornamental shrubs, as well as trees and creepers.
Chlorosis is also common on culture. The veins of the leaves of the diseased shrub remain green, and the plate turns yellow. The reason is iron deficiency or alkaline composition of the nutrient medium.

To make the soil more acidic, it is recommended to add some peat or substrate for rhododendrons to the trunk circle. Fertilizers with iron chelate are very useful. After a few weeks, the plant will restore the original color of the leaves.
Pests and the fight against them
In order for the shrub to remain a decoration of a garden or flowerbed, pests or the development of diseases should not be allowed on it. At the first sign of infection, the owner needs to act quickly. The speed of measures taken will prevent the spread of infection to neighboring plants.
Parasite insects found on hydrangiae:
- Spider mites. These are the most common crop pests. They are invisible to the naked eye, only the cobweb in the forks of the trunk and black dots on the surface of the leaves report infection, which a little later dry out and spill out, forming holes. Ticks breed especially quickly when the bush is located in an open, sunny place, and the soil is very dry. To get rid of them, sometimes a water shower is enough. If this method has not yielded results, it is recommended to treat hydrangea with a spray containing rapeseed oil. In the same way, re-infection can be prevented by periodically repeating the procedure for preventive purposes.

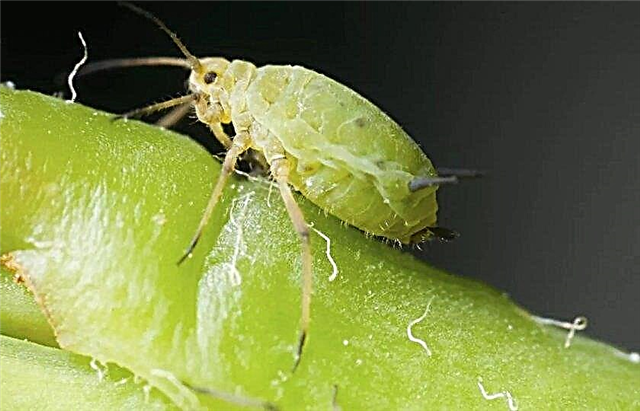
- Aphid. Appears on a shrub in the spring, in very warm and dry weather. Black insects are clearly visible on a bright green background. Their colonies are occupied by young, non-lignified shoots and the lower part of leaf blades, covering them with honey dew (the result of vital functions), which contributes to the development of fungal diseases. Parasites feed on cells and hydrangea juice, which slows down its development and worsens the decorative appearance. In most cases, it is enough to wash the bushes with a jet of water under pressure from a hose. If the measures taken did not lead to the expulsion of the pests, the aerial part is sprayed with an insecticide ("Karate", "Aktara").

Despite the high requirements for care and poor winter hardiness, gardeners should still engage in the cultivation of broadleaf hydrangea. This perennial shrub has a high decorativeness and decorates the site not only with elegant inflorescences of various shades, but also with a green mass of branches and large leaves.