Cucumbers are grown everywhere by plant growers. This vegetable is considered traditional for the cuisine of many countries, therefore it is cultivated from the hot south to the cold north. In addition to the usual varieties, there are many different plant hybrids. Next, it will be considered what Ginga F1 cucumber is, and its main advantages over related varieties are also described.
Grade description
Ginga cucumbers F1 (the designation "F1" indicates a hybrid origin from two different varieties) are mid-season cultivated plants of German breeding. The hybrid is universal, intended for open ground and cultivation under controlled conditions. Zoned cultivar in the Central Black Earth region, as well as in adjacent territories.
The plant is a parthenocarpic long-braided bush with numerous ovaries. It is medium-sized, forms small leaves of saturated green color. The shape of the leaves is heart-shaped, five-lobed. The stem is often creeping, with a rough surface, a height of about 1-2 m, ends with antennae.
Fruit characterization
Fruits are formed cylindrical in shape, rounded at the edges. They grow small, up to 10-15 cm in length with a width of about 3-4 cm; differ in a smooth peel with a slightly ribbed surface. On top of the peel, a slight pubescence of white color is often formed. The color of the fruit is mainly dark green, short white stripes develop over the main color.
Productivity of the variety is quite high and is in the range of 2.5–5 t / ha. The average weight of the cucumber is 90–100 g. Taste qualities of the fruits are high; the harvest is juicy, elastic and crisp. The output of marketable products is at least 88%.
The collected cucumbers are versatile, they are ideal for fresh consumption, as well as for preparing all kinds of dishes, including canned food.
Advantages and disadvantages
- The main advantages of the variety:
- increased productivity;
- flowering female type;
- resistance to powdery mildew and olive spotting;
- early harvest;
- the versatility of the fruit;
- good yield of marketable products.
- There were no serious flaws in the variety, with the exception of the need for specific agricultural cultivation techniques and in the formation of bushes. In addition, often the disadvantages include the high cost of seed.
Agrotechnics sowing and growing
The Ginga F1 hybrid was liked by vegetable growers due to its versatility and unpretentiousness - the plant can be successfully cultivated both in open ground and in protected conditions (greenhouse). However, in each individual case, this requires the observance of special technology and growing rules.
In the open ground
In open ground, cucumbers are often grown in seedlings, otherwise the plants will not have time to fully develop and give an abundance of fruits. Begin cultivation of cucumbers in the open ground with growing seedlings. Start sowing seeds in the second half of April. To do this, use both an individual small container and common trays, while the depth of the containers should be at least 8-10 cm - this helps to avoid diving into a new container, which often leads to the death of a third of seedlings.
Sow seeds only in nutritious and loose soil, any fertile substrates from flower shops are suitable for this. Alternatively, you can use a mixture of equal parts of peat, sod land and vermiculite (can be replaced with perlite or river sand). For 10 l of such a substrate, add 1-2 tbsp. l nitrofoski and 2 tbsp. wood ash.Did you know? The history of cucumber cultivation has about 6 thousand years. The homeland of the plant is considered to be the southern regions of India and the foot of the Himalayas, where it is still found in the wild form today.
Before sowing, the soil is sterilized, for this it is optionally soaked with 2% potassium permanganate, roasted in the oven (at + 125 ° C, about 30 minutes) or kept for 2-3 days in a freezer (at -25 ° C). After this, the substrate is kept at room temperature for about a week, and only then it becomes suitable for sowing.
Preparing for sowing requires seeds. First they should be sterilized: the procedure is carried out by soaking in specialized solutions, which can serve as 70% alcohol (up to 10 minutes), 2% potassium permanganate (20-30 minutes) or a solution of Fitosporin (10-20 minutes). Next, the seeds need to be activated - for this they are wrapped in moist tissue and kept at a temperature of about + 20 ° C for 2 days. Then they are moved to the refrigerator, where they are stored for about a day, after which they are directly sown.
Seeds are sown in a row-wise way - rows or small holes about 4 cm deep are created in the planting tank, and the distance between them should be about 6 cm. The crops are loosely covered with soil and then well soaked with water.
In the future, cucumbers provide standard care:
- temperature +22 ... + 26 ° С;
- regular watering - the soil should not dry out, so water the crops every 4 days;
- loosening the soil to a depth of 3-4 cm;
- daylight hours for at least 12 hours (crops need to be additionally highlighted).
Did you know? In ancient times, cucumber was one of the most popular vegetable crops. It is even mentioned in the Bible as a traditional vegetable of Ancient Egypt.
After the seedlings are extended to 15–20 cm, and at least 4-5 leaves are formed on the plants, seedlings can be transplanted into open soil. This period usually begins in 20–25 days from sowing seeds. In this case, the average daily air temperature should be no less than + 15 ° С. In the temperate climate zone, this period often begins in the middle or second half of May. Plants are planted according to the 40 × 50 pattern (holes are rows), while every 2 rows in the plot create a passage at least 80 cm wide.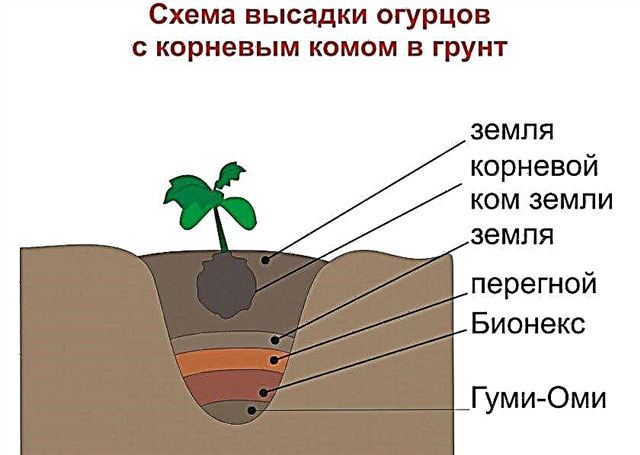
In the greenhouse
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse is one of the most common methods for creating optimal conditions for a crop on a site. This is especially important for the northern regions, with short and cold summers.
Sowing begins with soil preparation in a greenhouse. To do this, remove all pollutants from it, as well as the remains of vegetation, dig it well to a depth of 30 cm, and then pour it with a 2-3% solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid.
As soon as the soil dries, you should break the area for sowing. Plants are sown in a row-wise way, so parallel grooves are cut on the soil with a 40 cm inter-furrow space and a depth of 10 cm. An inter-row passage of 80 cm is created every 2 rows (for the convenience of caring for the plantations). Right before sowing, the rows should be well fertilized: for this, they are half filled with fresh manure, after which they are covered with a 2-3 cm layer of soil and well watered. Before sowing, they also prepare seeds - they do it the same way as in the case of growing seedlings.
After excess moisture is absorbed into the soil, seeds are sown. Sowing is done so that the seeds in a row are located at a distance of 20 cm from each other. To do this, in each row create additional recesses (about 10 cm) in each of which at least 2 seeds are placed. This is required in order to avoid low seed germination.
To seed sprouted as quickly as possible, the beds provide moderate hydration and a stable air temperature. As soon as several leaves appear on young shoots, the beds are thinned out. After the procedure, no more than one, the most developed and active plant, should remain at one growth point. Otherwise, plants rooted nearby will compete for soil space and nutrients (fraught with low productivity).
As soon as young cucumbers form 4-5 leaves, they can be transferred to standard care.
Important! If you use stationary hotbeds and grow cucumbers in a monoculture, then every 3-5 times it is necessary to change the soil (top layer 30 cm). This will protect the beds from low productivity and the invasion of pests.
Care Features
Regardless of the method of cultivation, Ging F1 cucumbers require standard growing conditions. They include soil care, timely fertilizers and regular watering. In this case, special attention should be paid to the formation of the bush, without which it will not be easy to achieve increased productivity and early ripening of fruits.
Watering and fertilizing
The cucumber fruit is 90–95% water, therefore, in case of lack of moisture in the soil, the plant will not be distinguished by high and high-quality crops. Irrigation should be carried out regularly. At first, young plants are watered sparingly, only after the soil is slightly dry - this is a prerequisite, since waterlogging of the soil will lead to rotting of the root system. However, less than 1 time in 5 days, it is not recommended to water the beds.
Watering begins more regularly after the young bushes give at least 7-10 leaves. From this moment, until the end of the vegetative period, the soil should be provided with moderate hydration with minimal fluctuation in soil moisture. Otherwise, the plant will form small and bitter fruits. Depending on the air temperature, this will require at least 2-3 procedures per week. But during a drought, irrigation is done daily.
The first feeding of cucumbers is done in the phase of 7 leaves. If the vegetable is grown in seedlings, the time favorable for this occurs 2 weeks after planting the seedlings in open soil. The first feeding should contain a high nitrogen content, therefore, solutions of cow manure (1:10) or chicken manure (1:15) are used for this, with a flow rate of about 5 l / m².
The second time the beds are fertilized after the plantations begin to bloom. At this time, cucumbers need a liquid mineral mixture, they are prepared from 40 g of superphosphate, 30 g of ammonium nitrate and 20 g of potassium nitrate (per 10 l of water). The resulting solution is used for radical irrigation, the calculation of the working fluid should be about 5-8 l / m².
During fruiting, cucumbers need an increased content of potassium and phospho in the soilpa To fill the deficit of these elements, superphosphate (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water) and potassium nitrate (20-30 g per 10 liters of water) are used, with a flow rate of 5 l / m². It is permissible to do such dressing every 10 days, while fertilizers alternate, which helps to create better conditions for the crop.
Important! Top dressing is done only in dry weather. If at the time of fertilizer a rainy period is observed, then crushed wood ash is used for fertilizer, with the calculation of 1 glass / m² of plantings.
Garter and bush formation
Cucumbers are tied up after about 7 leaves are formed on the bush. For this, an individual peg of metal or wood, about 1.5 m high, at a distance of 10 cm from the bush, is installed near each plant. As an alternative, you can use a common trellis - it is a rod fixed at a height of 2 m above the beds. As its support serve 2 horizontal posts fixed on the edges of the beds. Plants are attached to the trellis using strong twine, which is tied to the bar with one edge and the other with a small peg mounted near the plant.
Cucumbers also need quality formation. Do this as follows:
- in the zone of the first 2-3 leaves of the basal zone, all lateral growth points are removed;
- in the middle of the stem, in the area of every 3-4 nodes, the growth points are removed, while leaving 2 leaves and 2 fruiting shoots;
- at the top of the bush leave no more than 3 fruiting shoots. If necessary, the tip is thinned out, while no more than 3-4 leaves should remain on the plant.

Soil care
Soil care in cucumber stands is a mandatory measure that allows you to create the necessary soil microclimate, as well as protect the bushes from all kinds of pests. Weeding and loosening are often combined, making the procedure at least 1 time per week, to a depth of 10 cm. At the same time, the remains of weeds and their root system are necessarily removed from the beds.
The best time for loosening and weeding is considered to be 2-3 days after watering, which helps to avoid drying out of the substrate. But they can also be carried out the day after irrigation. The best period for soil care is considered to be early morning, but cultivation is permissible in the evening.
After weeding and loosening the beds, you need to mulch. The procedure makes it possible to protect plants from drying out, as well as create the necessary temperature regime in the soil. For this, a trunk circle with a diameter of 30 cm is created around the trunk of each bush, which is densely covered with covered material, a layer of 5-10 cm.
As mulch can serve:
- sawdust;
- coniferous bark;
- spruce and pine needles;
- humus;
- expanded clay;
- special artificial materials (agrofibre, geotextiles, etc.).

Pest and Disease Control
Although Ginga cucumber F1 is classified as a plant resistant to characteristic ailments and pests, if agricultural machinery for caring and growing is not complied with, beds are infected quite often. The fight against diseases and pests should be started immediately, since in just 1-2 weeks they can completely destroy the plantings.
The most common cucumber infections:
| Title | Ways to fight |
| Anthracnose | Affected beds are treated with copper chloride, with the calculation of 40 g per 10 l of water |
| Bacteriosis | Infected plants are treated with solutions of copper chloroxide, with a concentration of 40 g per 10 l of water |
| Peronosporosis | When a disease occurs, cucumbers should be sprayed with a choice of 69% Acrobat MC, Ridomil MC 72%, Kurzat R |

Characteristic crop pests:
| Title | Ways to fight |
| Thrips | The beds are sprayed with the drug "Actellik", "Confidor" 20% or "Karate" |
| Ticks | Plantings are treated with a solution of "Actellica" 50% or "Talstar" 10% |
| Aphid | The best way to help handle the processing of insecticide "Confidor" 20% or "Karate" |
| Cucumber bugs | Solutions of "Confidor" 20%, "Karate" will help to eliminate the pest |

Harvesting and storage
Ginga’s first harvest of F1 ripens on average on the 45th day after the first seedlings, by which time the fruits will have a length of 10 cm. Cucumbers are harvested every 2-3 days, however, at the height of fruiting, the fruits are removed from the garden every day. Harvested with a sharp knife, which separate the stem from the bush.
The collected fruits are thoroughly cleaned of soil residues and other contaminants, and then washed under running water. Pure cucumbers are dried naturally and then transferred to the refrigerator. The most optimal temperature for storing the crop is considered to be + 5 ° C, which allows you to maintain the freshness of cucumbers for 2-3 weeks. For longer storage, the fruits are salted.
Important! Fruits are washed only with cold water, with a temperature not exceeding + 20 ° С. Warm and hot water will damage the tissue of the cucumber, which at times reduces the stubbornness of the crop and its marketability.
Ginga F1 is a great example of highly skilled selection of fruit crops. The plant is suitable for fruiting in almost any climate, while it is characterized by high productivity and quality of fruits. This makes it possible to effectively use the hybrid for both home and industrial vegetable growing, including as a raw material for conservation and other processing.












